Supply Chain Management in Beef Market
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic adversely affected many sectors of life, taking a huge toll not just on the economic system but the livestock manufacture, such as global meat production and supply chain. Several countries' preventive measures included travel restrictions, border controls, and country lockdowns, developed harsh consequences affecting production and supply chain. Meat production and processing were compromised due to difficulty of purchasing production inputs such every bit feed for animals, restrictions of transportation of live animals including seasonal border crossing restrictions, accessing professional services and workforce, and restrictions in supplying meat and meat products to the markets (1–3). These problems acquired a drop in capacity for meat product and plants' processing, resulting in decreased sales conditions that slowed downward marketplace activity (4). Furthermore, during this COVID-19 pandemic, there was a decrease in governmental capacities to forestall, control and care for brute diseases. This was mainly due to the reallocation of the resource needed to respond to the pandemic effectively. Particularly, prevention and command of transboundary diseases such every bit Foot and Mouth Illness, African Swine Fever, Avian Influenza, and other infectious animal diseases take been severely compromised meat production and supply chain (v).
The COVID-19 virus rapidly spread among meat constitute workers due to prolonged contact with infected co-workers, inability to follow social distancing at the workplace, shared working areas, and common transportation methods to and from work. These infected workers caused the spread of illness at community levels (6). Therefore, many plants began to close temporarily to terminate the spread of illness on a larger calibration. The endmost of these facilities contributed to the sharp turn down in the supply chain, leading to decreased meat production capacities (7). The production chapters loss reached 25–43% for beef slaughterhouses in the United States (8).
The prices of meat and meat products likewise fluctuated due to a gap in need and supply, mainly due to panic buying and lockdown restrictions. Therefore, this review aimed to highlight the impact of COVID-19 on meat production, supply concatenation, and cost fluctuations. This will exist helpful to formulate future recommendations to ensure a stable meat supply chain. It will also help livestock farmers, animal health professionals, abattoir workers, meat processors, traders, and policymakers to effectively combat worse situations in the hereafter.
Origin of COVID-19
The SARS-CoV-2 is a newly identified virus that caused the outbreak of pneumonia in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Inside no time, SARS-CoV-2 was isolated on January 7, 2020, and complete sequencing was performed. Initially, the Globe Health Arrangement (WHO) named the coronavirus as the 2019-novel coronavirus (COVID-19) on Jan 12, 2020. It was reported that the genome sequence of COVID-xix is quite similar to a bat CoV RaTG13 and has 96.2% identity and 79.5% similarity to SARS-CoV as well. Afterward studying the genome sequence results and evolutionary analysis, bats were assumed to be the virus'southward natural hosts. Additionally, it was also assumed that SARS CoV-two might be transmitted from bats via unknown intermediate hosts and finally infecting the homo race (ix).
On January 5, WHO warned the world nigh implementing travel restrictions from Communist china due to this pandemic. The start death was reported on January 11 due to COVID-xix. The infamous COVID-19 was declared a public wellness emergency on Jan 30, 2020, due to its rapid spread and severity. It was declared equally a pandemic on March eleven, 2020, by WHO. The near common signs shown past affected patients with COVID-19 were fever, cough, and rare gastrointestinal infection (10). Later on the outbreak of COVID-xix in Wuhan, it rapidly spread worldwide and affected all sectors of life. Meat industries besides severely affected and disrupted production and supply concatenation. The impact of COVID-xix on meat product and supply chain is shown in Figure 1.
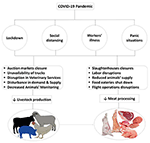
Figure one. Impact of COVID-nineteen on meat production and supply chain.
Impact of COVID-xix on Meat Production
The COVID-19 pandemic has straight and indirectly impacted overall meat production. Through the infected workforce causing the shutdown of meat plants, there was a decrease in product, processing, distribution, and marketing potential (8). Farmers faced difficulty when searching for a more than suitable market to sell their animals. The sale of expensive primal meat cuts was decreased due to the temporary shutdown of food eateries which affected the income coming in from meat and meat products (11). Furthermore, the decreased income status of consumers likewise affected meat production (12). During these circumstances, a decrease in meat production went from 338.9 1000000 tons (carcass weight) in 2019 to 333.0 million tons in 2020 (5, 13). The pandemic'due south initial estimated impact on the beef industry is around $13.6 billion, with additional influences that can occur in the hereafter (14).
The short-term impact of COVID-19 on Spanish modest ruminant flock production was investigated (15). To which, the authors observed the sudden impact on meat markets, specially in pocket-sized ruminant flocks. The observations depicted a 25.9% drop in slaughtering activity of lambs and 28.5% for goats in April 2020 compared to the slaughtering information of April 2019. On the other hand, the slaughtering activeness for sheep and goat kids was higher in March 2020 compared with March 2019. In some other study, researchers found significant differences in the pandemic's comparative influence in different classes (steer, heifer, dairy cows, beefiness cows, bulls, and hogs) of animals and slaughtering volumes in different regions of the The states. In May 2020, steer and heifer slaughtering volumes were 41% lower when comparing to May 2019. The biggest hit was observed in the final week of April and the first week of May 2020; the processing numbers for pork and beef declined by 40% compared to the aforementioned periods of 2019. During an 8-calendar week study starting April fifth, cattle slaughtering was reduced by 1.fourteen million head, which is 22% lower than the prior year. There was a xiii% reduction (2.36 million caput) during those 8 weeks compared to 2019 (16) for pork. It was reported that North American meat processors that had to deal with this abnormal situation were committed to paying the extra money to retain butchery workers ($2 per 60 minutes premium and $500 bonus to all workers capable of completing consecutive shifts for 8 weeks) and attract livestock farmers to maintain the supply of animals (17). The overall global meat production and merchandise per centum year-on-year is given in Table 1.
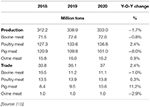
Tabular array 1. Globe meat production, merchandise and percentage twelvemonth-on-twelvemonth (Y-O-Y) change.
Concerns of Meat Producers
The impact of COVID-19 on livestock product was unexpected. Due to this pandemic, meat packaging facilities also closed or reduced working hours, affecting processing capacity throughout the country. Many animals could not exist processed, which resulted in huge losses to the producers. Poultry processors were directed to depopulate their sheds. Nigh of the meat processing plants were forced to work at reduced levels than their average capacity; in the United states, grunter, and cattle slaughter reduced past virtually 40% in April 2020 compared to Apr 2019. There was a positive shift for mid-sized and pocket-size slaughterhouses and processing plants that ensured the availability of regional and local meat and poultry supplies during a pandemic. Unfortunately, at the same time, harvest facilities at smaller levels were insufficient to encounter the demand from farmers or breeders that now have no market due to extensive plant closures, fifty-fifty while small plants function at maximum capacity (xix).
The American Subcontract Bureau Federation conducted a survey that revealed an 84% of Americans hoped the government would provide financial assistance to farmers to keep them motivated during the pandemic (xx). In India, farmers are no more unfamiliar with this type of emergency, but the electric current disturbance washed by this virus outbreak is unmatched. The poultry sector that employs 1.5 1000000 smallholder farmers observed the worst striking. Broiler meat demand vicious impulsively on reports associating them to COVID-19. In the early lockdown stage, all trades regarding the meat industry in the country were distorted. This distortion impacted livestock farmers and the poultry industry, to which both need a continuous cash flow for feeding their animals (21).
In developing countries like Pakistan, farmers could not move from villages to cities due to transportation methods' unavailability. They could not sell their animals in markets due to lockdown restrictions. Initially, the meat manufacture and associated slaughterhouses completely shut downwards. Even the cattle markets were not immune to sell the animals for slaughter at the local level. The shutting down of event venues, restaurants, and a ban on big gatherings, reduced the poultry demand by 20–25%. The ambiguity coupled with the absence of a articulate strategy from the government compelled farmers to sell out their birds or meat at a reduced toll and limit their losses. Too, farmers were too unclear most the abiding supply of feed for their animals and birds at commercial farms, resulting in several of them suspending purchasing hatchlings (22).
The sudden restriction and monitoring of human being activities could as well affect animal health due to hindrances in veterinary services' timely provision (23). These imposed restrictions on veterinary professionals, farmers, and workers' activities cause hurdles of monitor wellness condition and the daily requirement of animals. These scenarios resulted in the problems of overstocking at many farms that compromised animals' allowed systems and increased the chances of disease outbreaks. Some farmers culled their animals to reduce the animal population, which limited animal product production (8). Feedlot cattle prices suffered the near significant striking than cull cattle and feeder cattle. For case, feedlot cattle prices barbarous by 16% compared to the 9% decline in feeder cattle prices.
Impact of COVID-19 on Meat Processing
Covid-19 showed a massive impact on the global meat processing sector. Firstly, this sector is labor-intensive, which is why it can be drastically affected by workforce disruptions. Secondly, due to food eateries being shut down, a lot of storage infinite is required to accommodate all the meat products due to air travel restrictions for international merchandise, which is not possible for almost affected countries. In the US, the shutdown of processing plants began on March 27, 2020, with the endmost of poultry processing facilities followed by a cascade of closing of beef, poultry, and pig processing facilities over the next couple of weeks. These closings led to reduced slaughter and processing capacity and a 45% decline in hog processing, with a similar impact on other meat product species being observed (iv, 24), studied the touch on of a pandemic on American and Brazilian meat sectors and demonstrated that meat processing was incredibly confusing during April and May 2020 due to the virus outbreak at slaughtering facilities resulting in an extraordinary rise in livestock prices. Beef processors experienced a decline (21% in April and nineteen% in May) in production as compared to January-March 2020. In June-August 2020, the product level was near the highest level observed before processing facilities shutdown. Similarly, the pork processing industry declined (18% in Apr and 19% in May) compared with production in Jan-March 2020. The U.s.a. beef and pork processing industry was declined past xl% during April and May 2020 compared to 2019. In Canada, 75% of beefiness processing plants were disrupted due to the shutdown of meat facilities, particularly in the Alberta province (25). In Ghana, Covid-19 harmed the industry past inputting supply issues every bit the country depends mainly on importing livestock from the U.s.a., Brazil, and the European Wedlock. Therefore, the decline in cattle, sheep, and caprine animal numbers was 57, 61, and 64%, respectively, during the lockdown menstruation (26).
Concerns of Processors
The COVID-19 outbreak has afflicted different societies and has caused far-reaching consequences, hence the demands of serious public health interventions and measures. Similarly, meat processors take faced many problems, including illness among plant workers and the closing of meat facilities.
Illness Amidst Establish Workers
COVID-19 transmission and chances of respiratory diseases are generally college for the people involved in congregate work atmospheres. Meat and poultry facilities have a besiege work environment. Worker rubber in such settings needs a particular focus, especially during respiratory disease outbreaks (27). CDC aggregated qualitative information from risk assessment of plants in May 2020. They reported 115 meat and poultry processing plants' data indicated that COVID-nineteen cases were present in 19 out of 23 states of the USA compared to 9 to 27 from April 2020. A total of 4,913 (3%) of 130,578 workers were diagnosed COVID-nineteen positive, ranging from 0.half-dozen to 18.two%, while 20 deaths were recorded due to the virus in 19 states of the United states by April 27, 2020 (28). A total of 129 out of 300 workers were reported COVID-19 positive at ane of Portugal's leading poultry slaughterhouses (29). Outbreaks in England and Wales have also been associated with the meat processing sector in Anglesey, Merthyr Tydfil, Wrexham, and Kirklees (xxx). The possible reason to control the COVID-19 at meat plants was the facility barrier (structural and operational) confronting its control. It was challenging to maintain a six-foot altitude in the working premises, practicing applied disinfection guidelines and send conditions (31). In the future, screening workers with COVID-nineteen symptoms, medical leave policies, improved disinfection, use of cloth masks, increased number of vehicles, decreased passengers to vehicle ratios, irresolute transport to or from the establish premises to reduce virus exposure, and mitigation efforts are some practical strategies to limit the asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic virus spread to the customs (32), as well every bit to keep the normal health status of the workers to preserve the critical infrastructure of meat and poultry industries (33).
Therefore, information technology is recommended to ensure a collaborative arroyo of public health and precautionary biosecurity measures for workers in the field of meat and poultry processing for their self-protection, comeback of nutrient safety, and preservation of meat production at processing facilities during the pandemic in the future (34).
Meat Found as a Hotspot
Slaughterhouses and meatpacking plants were major threats for spreading the COVID-19 infection throughout the pandemic (35). It is noteworthy that the socio-demographic and labor force factors involved in COVID-19 outbreaks include young workers having more than chances of asymptomatic COVID-19 disease, which are housed in short congested rooms, transported on overcrowded vehicles under inadequate or non-existent hygiene measures (36). Additionally, the traveling of employees to and from far-off rural areas in the meatpacking facilities was another cistron for the increased transmission of COVID-xix (37). In May 2020, half of the COVID-19 hotspots in the Us were contracted within meat processing facilities where livestock was slaughtered and packaged in the closed areas. Furthermore, the virus proliferates higher at cold temperatures and high relative humidity, which are meat processing plants' characteristics (38). Metallic surfaces retain alive viruses for longer than other environments (39, 40). Workers in proximity with others crave to speak loudly over the running processing line'south dissonance, which causes the release of more droplets and disseminates them farther effectually the community (41). Several reports have suggested that the COVID-nineteen virus ascension surged in meatpacking plants in several different countries, including the United states of america, Canada, Frg, Spain, Ireland, Brazil, and Australia (42).
Shutdowns of the Meat Establish
The touch on of COVID-19 on the livestock sector, allied fields, like the food chain, and farmers was completely unforeseen. Infected cases of workforce in meat plants grew apace to impart ruthless effects on humans and the welfare of the surroundings in different countries. In the United States, meat processing plants especially poultry and pig facilities shut down when they came to know virtually major outbreaks. The processing capacity of pigs has been reduced up to 45%. Producers or farmers were compelled to cull their healthy animals on the farms due to the lack of animal feed supply. Disposal of the carcass was also connected with possible biosecurity risks and unfavorable effects on the environs (43). The clan of spread of the virus from vectors was found predominantly among large processing plants and large meatpacking companies. Withal, evidences were institute that plant closures decreased cases and plants that received consent from the US Department of Agriculture to increase their production line reported more cases amidst workers (44). Due to close down of meat plants, the production was decreased by at to the lowest degree 25% (45).
Impacts of COVID-19 on Meat Supply Chains
Covid-19 has drastically afflicted the meat product, processing, distribution, and consumption phases of the global meat supply chain due to lockdowns and restrictions taken by diverse governments. Illness of the establish workers led to the suspension of meat processing and packaging plants in various countries (7, 46). This situation decreased the production capacity upwardly to 25, 43, and 15% of beefiness, pork, and chicken industries, respectively (47). Furthermore, instead of slaughtering continuously at the aforementioned rate, many animals were euthanized. Concomitantly, it is expected that the economic losses to the beef industry reached $13,617,418,450 (48), which causes severe economic losses, especially to the meat producers and processors.
In Brazil, more than two,400 slaughterhouse workers were diagnosed equally COVID-19 positive from different slaughterhouses around the country. In England, diverse meat processing units were suspending their operations after 246 confirmed cases of COVID-19 appeared in England and Wales (7). Almost one,553 confirmed cases were reported at meat processing plants in Deutschland. France faced a 30% reduction in staff availability in meat processing facilities due to COVID-19. Furthermore, meat processing and packaging plants have besides been affected due to physical distancing rules and less labor availability. In the United states of america, more than ten million hogs were eliminated from the meat supply chain from Apr to September 2020. This scenario created a shortage of about 2 million pounds in the market that was more than 7% compared to the total product of the final twelvemonth (46).
The decrease in meat production, processing and supply chain resulted in higher prices of meat and meat products. Therefore, the meat purchasing ability of poor and heart-class families was reduced that contributed to food insecurity. In China, meat production was reduced due to meat facility workers' quarantine, resulting in a decreased supply chain and increased meat prices in the local Chinese market place, such as the Xinfadi market in Beijing (49). Some supermarkets have limited the number of items such as beef and pork. Furthermore, the nutrient points also stopped serving certain products such as beef burgers.
Due to COVID-19, meat producers and processors accept lost access to local and international markets for selling their products. The consign restrictions accept disturbed global trade as well. Many Asian countries, including the Lao people's democratic republic, Thailand, Myanmar, and Vietnam, were unable to export their livestock and frozen meat products to Red china (8). Similarly, the beef and veal consign from Kingdom of denmark in Europe was significantly decreased due to the COVID-xix. The limited meat product also impacted the distribution of meat products and the supply chain. One of the significant factors that afflicted meat distribution was the restricted transportation laws due to lockdowns. In the Philippines, the filibuster of transportation of the raw material for meat processing created the meat shortage until the ban was loosened (eight). Meat and its products are generally transported beyond the borders through cargo ships. The cargo charges have been significantly increased while the product price has decreased due to COVID-nineteen. Several meat processing plants reported higher shipment costs of meat and its products (49). Alive creature transportation was also affected by the restricted movements and edge checks that affected the business and compromised animal welfare (50). Overall, global trade was decreased by thirteen–22% during the few months of the pandemic's emergence.
The restricted movements have besides threatened people's livelihood, mainly in developing countries such every bit East Africa (eight). In these countries, many livestock producers rely on the export of live animals and frozen meat to the Middle Eastern countries during specific occasions such as Ramadan and Eid-ul-Adha'due south religious events. Last yr, on these occasions, these people were unable to access the markets for selling their animal and frozen meat due to lockdown restrictions. Pakistan also restricted the open markets for animal sales at Eid-ul-Adha, 2020. Therefore, many people cull the online platform for the sale and purchase of animals on such occasion that was new for them, which over again created bug. All these situations showed an adverse effect on meat supply chains during COVID-19.
Changes in Consumer Behavior
Consumers normally interact with the stop production presented on the shelves of supermarkets. However, the COVID-nineteen pandemic has changed the purchase and consumption of meat and its products mainly due to the decreased purchasing power, staple priorities, and safety awareness among consumers. Most half of the meat is sold in the grade of nutrient segments (educational institutes, offices, hotels, and restaurants). The closure of the educational institutes and restaurants showed an agin upshot on the supply and distribution of meat and its products (51). Furthermore, working from domicile has increased the consumption of meals at home that dropped the restaurants' need. Additionally, the number of visits to superstores and spending money per visit was also changed due to COVID-19 (52). The change in unlike product consumption past the consumers during the COVID-xix pandemic is given in Figure 2.
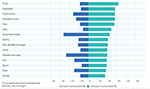
Figure 2. The change in product consumption by the consumers during COVID-xix pandemic [Source: (53)].
The pandemic outbreak also interrupted the routine life of the people. Staying at domicile for longer durations resulted in higher consumptions of carbohydrates, fatty, and proteins. The stress of quarantine measures pushed the people toward using more sugar-based diets for feeling motivated and positive because the food items increase the production of serotonin to combat stress (54). The demand for hamburgers increased during the pandemic as well. Higher demand for minced meat increased the price up to $4.74 per pound during the pandemic pinnacle. Similarly, pork and craven's retail cost was increased by $4.25 and 1.75 per pound, respectively.
Consumers besides started to stock items that accept longer shelf life during COVID-19. They too experienced the reduced availability of certain types of food items. In European countries, flour is the product that attained more attention due to home-cooking, which atomic number 82 to its shortage in the market during the initial few months of the pandemic. The prices of the staple items were as well increased due to the panic buying. Consumers preferred take-out or domicile commitment options rather than having a repast in restaurants due to lockdowns (52). Consumers found limited meat preparations in supermarkets due to pandemic. Therefore, it was time to invest in plant-based meat alternatives or in cultured meat to combat this blazon of situation in the futurity. Response rates for consumer price index for meats, poultry, and fish was decreased from 91 to 61%, and for beef and veal was declined 93–61% from June 2019 to June 2020.
Meat Price Fluctuations
The meat products prices increased due to demand and supply issues; panic buying resulted in empty shelves. The producers were unable to supply enough products due to the closure of meat processing plants (seven). Akter (55) presented that nutrient prices in European countries significantly increased during March and April 2020, especially in countries with high restrictions, while the prices became stable in May. Pandemic had a massive bear upon on meat products, mainly pork's price in Beijing and Hubei provinces, which were severely hit by the virus. The peak prices were observed from January to Apr 2020. The highest price variations were noticed in Beijing (56). The impact of COVID-19 on price fluctuations of different meat types in dissimilar world regions is given in Table 2.
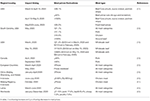
Table two. Impact of COVID-nineteen on prices fluctuations of different meat types in different regions of the world.
In a recent study (57), highlighted COVID-19 impact on USA beefiness prices. The first wave of increase in prices was mainly due to lockdown effects starting from March six to Apr 10, 2020, up to a 39.1% increase in prices, particularly beef cuts (i.e., chuck, round, brisket, and loin strips) extensively used in ground beef production due to more than need for footing beef in the state contrarily, there was pass up in primal cuts (i.e., rib eye and tenderloin) prices up to 42% due to closure of food eateries. The second wave was more pronounced due to reduced beef product from Apr x to May 8, 2020, upwards to a 150% increase in meat cuts prices (58), studied the meat supply chain issues in South Carolina, USA. The meat prices increased to 21.7% by the terminate of May 2020 due to contraction in meat supply; the increase in pork and craven prices was 17.7 and ten.5%, respectively. The highest toll jump (>100%) was observed in ground beef in May 2020 compared to previous months. In another comprehensive report virtually meat prices in the USA, at the terminate of March 2020, the wholesale prices jumped to $255/cwt compared with $210/cwt before March prices. This increase in prices was mainly due to panic buying leading to increased need at grocery stores. The wholesale price kept increasing, reaching the highest recorded price of $459/cwt on May 15, 2020, due to a refuse in meat product and shutdown of meat processing plants (16). The monthly percent changes of price indexes for meat, poultry, and other animal products from Jan to June 2020 is given in Table 3.

Table 3. The monthly pct changes of price indexes for meat, poultry, and other animal products from January to June 2020.
In contrast (59), reported a decline in meat (pork) prices in Canada compared with the baseline values, starting in the last week of March 2020, the lowest prices (twoscore% pass up) were recorded in mid-Apr, which could exist due to closure of food eateries. After, the prices started increasing; the highest prices (40% increase) were observed in Ontario during September 2020, possibly due to a subtract in meat processing. Similarly (63), found that in 2020, the international meat product prices decreased by 7–18% compared to their baseline values. It is mainly due to the slowdown of the global economy due to travel restrictions. The highest declined was observed in pork prices (17.6%), followed past beef (ten.4%), sheep (seven.3%), and least in poultry (7.0%). In 2021, at that place is an increment in pork and sheep while beef and poultry are even so below their regular prices. The authors estimated that all meat production prices would exist shut to their baseline prices past 2025 (sixty), also reported chicken meat prices declined in Indonesia during June-July 2020. The lowest price, Rp.14730/kg, was recorded from March 19, 2020, to July, compared with 2019. This subtract of Rp.930/kg of meat prices was primarily due to less need and oversupply issues (61), also studied chicken prices in Malang Regency, Indonesia. They witnessed the decline in chicken meat prices mainly due to demand and supply problems (62), discussed the COVID-19 impact on the Latvia meat sector; the export and local need of meat products decreased from March-June 2020, leading to increased meat stocks products ultimately, a decline in prices, and ultimately, reduced revenues generations.
Conclusions
The speedily evolving nature of the COVID-nineteen virus created many problems for the meat manufacture. The limitations on animal exportation, logistics restrictions, and the shutting downwards of slaughterhouses, restaurants, and food services adversely affected all stages of the meat supply chain. Farmers were unable to find a suitable market to sell their live animals. Meat processing capacity also decreased due to the closure of the processing plants. The availability of meat and its products for the consumers was as well compromised due to establish closures and panic buying, resulting in fluctuations in prices. Therefore, the following suggestions are proposed to maintain the different stages of the supply chain in social club to combat such drastic situations in the future:
In the future, the following precautionary measures and practical recommendations should be followed to reduce the affect of such devastating pandemic situations and ensure continuity of meat production and supply concatenation: (ane) livestock farmers should (i) communicate with suppliers of consumables, feed distributors and professionals such as veterinarians and meat processors to notice solutions to secure inputs supply, subcontract services, and meat supply chain; (ii) talk with farmers associations to reach out the policymakers for getting the compulsory exemptions for transportation of feed, animals, and personnel; (ii) adopt strict precautionary and management measures at farms to avoid affliction spread. (two) Professionals should (i) secure continuous services at farms to ensure animate being wellness; (ii) upwards to date with the knowledge near the pandemic and aid farmers to ensure farm biosecurity. (3) Meat processors should (i) adopt online business models for a continuous supply of meat nether such conditions; (ii) introduce mod automation at the plant to reduce labor interest for sustainable meat production. (4) Policymakers should (i) develop the policies to reduce the effect of such pandemic on meat production and supply concatenation; (ii) communicate with the government to ensure continuous normal period of inputs and outputs of the meat production organization; (3) review the existing animal disease prevention and control policies; (iv) take steps to control the food and meat prices in the market; (5) communicate with across the border governments to facilitate the controlled transportation or import and export of animals and farm inputs. (5) Meat scientists should look forward to developing cultured meat and plant-based alternatives to overcome nutrient insecurity nether such worst situations.
Writer Contributions
MI compiled the review materials, drafted the manuscript, contributed to the abstract, introduction, conclusions, future recommendations and involved in the review, and editing of the manuscript. MY contributed to the impacts of COVID-xix on meat supply chains, changes in consumer behavior, and contributed to review and editing of the manuscript. IB contributed to impact of COVID-19 on overall meat production and contributed to review and editing of the manuscript. SA contributed to the affliction among workers, meat establish as hotspot, and contributed to review and editing of the manuscript. MSI wrote the meat price fluctuations, and contributed to review and editing of the manuscript. MJ and ZH involved in writing-review of the first draft and contributed in revision of the manuscript. AS contributed to shutdowns of meat plants, concerns of farmers and processors, and contributed to review and editing of the manuscript. SU contributed to the origin of COVID-19 and contributed to review and editing of the manuscript. DG-R helped to amend the grammar, sentence structures of the manuscript, and contributed to review and editing of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absenteeism of any commercial or fiscal relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
6. Waltenburg MA, Victoroff T, Rose CE, Butterfield Yard, Jervis RH, Fedak KM, et al. Update: COVID-19 amid workers in meat and poultry processing facilities—United States, April–May 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2020) 69:887–892. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6927e2
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
8. Hashem NM, González-Bulnes A, Rodriguez-Morales AJ. Animal welfare and livestock supply chain sustainability nether the COVID-19 outbreak: an overview. Front Vet Sci. (2020) vii:679. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.582528
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
9. Zhou P, Yang Xl, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang Westward, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of likely bat origin. Nature. (2020) 579:270–3. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
10. Guo Year, Cao QD, Hong ZS, Tan YY, Chen SD, Jin HJ, et al. The origin, manual and clinical therapies on coronavirus affliction 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak – an update on the status. Mil Med Res. (2020) 7:11. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text
12. Rude J. COVID-19 and the Canadian cattle/beef sector: some preliminary analysis. Can J Agric Econ. (2020) 68:207–13. doi: x.1111/cjag.12228
CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
15. Vidaurreta I, de la Iron C, Orengo J, Gómez-Martín Á, Benito B. Short-term economical touch on of COVID-nineteen on Spanish pocket-size ruminant flocks. Animals. (2020) 10:1357. doi: 10.3390/ani10081357
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
eighteen. Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO). Biannual Report on Global Food Markets. (2020). Available online at: http://world wide web.fao.org/iii/ca9509en/ca9509en.pdf (accessed March 5, 2021).
24. Mallory ML. Impact of COVID-nineteen on medium-term export prospects for soybeans, corn, beefiness, pork, and poultry. Appl Econ Perspect Policy. (2020) 43:292–303. doi: x.1002/aepp.13113
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
27. Shaw KA, Szablewski CM, Kellner Due south, Kornegay L, Bair P, Brennan S, et al. Psittacosis outbreak among workers at chicken slaughter plants, Virginia and Georgia, USA, 2018. Emerg Infect Dis. (2019) 25:2143. doi: ten.3201/eid2511.190703
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
28. Dyal JW, Grant MP, Broadwater Chiliad, Bjork A, Waltenburg MA, Gibbins JD. COVID-19 among workers in meat and poultry processing facilities-19 States, April 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2020) 69:557–61. doi: x.15585/mmwr.mm6918e3external icon
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
32. Wei We, Li Z, Chiew CJ, Yong SE, Toh MP, Lee VJ. Presymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2—Singapore, january 23–march 16, 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2020) 69:411. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6914e1
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
34. Ebrahim SH, Memish ZA. COVID-nineteen–the role of mass gatherings. Travel Med Inf Dis. (2020) 34:101617. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101617
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
36. Durand-Moreau Q, Adisesh A, Mackenzie Yard, Bowley J, Straube South, Chan X. What Explains the High Rate of Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Meat and Poultry Facilities. Oxford: Oxford Center for Evidence Based Medicine (2020).
39. Van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH, Holbrook MG, Adventure A, Williamson BN, et al. Droplets and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 equally compared with SARS-CoV-1. North Engl J Med. (2020) 382:1564–seven. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2004973
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
41. Anfinrud P, Stadnytskyi 5, Bax CE, Bax A. Visualizing spoken language-generated oral fluid droplets with laser lite scattering. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:2061–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2007800
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
44. Taylor CA, Boulos C, Almond D. Livestock plants and COVID-19 transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2020) 117:31706–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2010115117
CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
52. Bakalis Due south, Valdramidis V, Argyropoulos D, Ahrne L, Chen J, Cullen P, et al. How COVID-19 changed our nutrient systems and food security paradigms. Curr Res Food Sci. (2020) iii:166–172. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2020.05.003
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
54. Muscogiuri 1000, Barrea L, Savastano S, Colao A. Nutritional recommendations for CoVID-19 quarantine. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2020) 74:850–i. doi: 10.1038/s41430-020-0635-ii
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
55. Akter S. The affect of COVID-19 related 'stay-at-home' restrictions on food prices in Europe: findings from a preliminary analysis. Nutrient Secur. (2020) 12:719–25. doi: 10.1007/s12571-020-01082-3
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
56. Yu Ten, Liu C, Wang H, Feil JH. The impact of COVID-xix on food prices in Communist china: evidence of four major food products from Beijing, Shandong and Hubei Provinces. Mainland china Agric Econ Rev. (2020) 12:445–58. doi: x.1108/CAER-04-2020-0054
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
58. Richards S, Vassalos Chiliad. COVID-19 amplifies local meat supply chain problems in S Carolina. J Agric Food Sys Comm Develop. (2020) 10:one–v. doi: ten.5304/jafscd.2020.101.001
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
59. Weersink A, von Massow M, Bannon N, Ifft J, Maples J, McEwan Grand, et al. (2021). COVID-19 and the agri-food system in the The states and Canada. AIMS Agric Food. (2021) 188:103039. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2020.103039
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
threescore. Nendissa DR, Wahib MA, Astuti MH, Arimbawa P, Kapa MM, Elbaar EF. Socio-economic impact of the Covid-nineteen pandemic: empirical study on the supply of chicken meat in Republic of indonesia. AIMS Agric Nutrient. (2021) half dozen:65–81. doi: 10.3934/agrfood.2021005
CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
61. Nurahmi South, Zalizar L. The impact of Covid-19 on chicken broiler farm business concern in Malang Regency. AMCA J Sci Technol. (2021) 1:17–nine. doi: 10.51773/ajst.v1i1.29
CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
62. Grinberga-Zalite G, Pilvere I, Muska A, Kruzmetra Z. Resilience of meat supply bondage during and after COVID-19 crunch. Emerg Sci J. (2021) 5:57–66. doi: 10.28991/esj-2021-01257
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
63. Elleby C, Domínguez IP, Adenauer Grand, Genovese M. Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global agricultural markets. Environ Resour Econ. (2020) 76:1067–79. doi: ten.1007/s10640-020-00473-6
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
64. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Import/Export Price Indexes. (2020). Available online at: https://www.bls.gov/mxp/ (accessed March 8, 2021).
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2021.660736/full
0 Response to "Supply Chain Management in Beef Market"
Post a Comment